Social Studies: Ancient Civilizations
We will study Ancient Civilizations in Social Studies. We'll start off the year learning about Ancient Humans and the agricultural revolution. Then we'll learn how farming lead to advanced civilizations in: Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, China, Greece, and Rome. Geography affected the success of all of these ancient civilizations. The earliest civilizations began around fertile river valleys because they were excellent places to grow crops, and therefore have a surplus of food. With a surplus of food, ancient people were able to focus on tasks other than obtaining food like developing religions, building architectural masterpieces, and establishing structured governments.
Ancient Humans

skeleton of Lucy
• Early humans were hunter-gatherers. They relied on animals and plants for food.
• They moved constantly in search of their food.
• Early farmers used slash and burn techniques.
• The coming of the Ice Ages caused people to adapt, including developing new clothing.
• After the Ice Ages, people began to domesticate plants and animals and build mud-brick houses, eventually leading to permanent settlements.
• They also began to specialize in different activities, including weaving cloth for clothes.
• They moved constantly in search of their food.
• Early farmers used slash and burn techniques.
• The coming of the Ice Ages caused people to adapt, including developing new clothing.
• After the Ice Ages, people began to domesticate plants and animals and build mud-brick houses, eventually leading to permanent settlements.
• They also began to specialize in different activities, including weaving cloth for clothes.
Mesopotamia
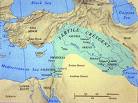
Fertile Crescent
• The yearly flooding of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers created rich soil allowing for good agriculture and early civilizations. However, the flood was unpredictable.
• New agricultural technique arose, such as irrigation through building dams, channels, walls, and ditches. These led to the rise of cities, religion, writing, science and math.
• Mesopotamia built temples and held religious festivals to please the gods.
• Hammurabi’s Code organized all laws, but was very harsh. "An eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth."
• Mesopotamian's wrote using cuneiform. Cuneiform was first used to keep track of trade.
• New agricultural technique arose, such as irrigation through building dams, channels, walls, and ditches. These led to the rise of cities, religion, writing, science and math.
• Mesopotamia built temples and held religious festivals to please the gods.
• Hammurabi’s Code organized all laws, but was very harsh. "An eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth."
• Mesopotamian's wrote using cuneiform. Cuneiform was first used to keep track of trade.
Ancient Egypt

King Tut
• In ancient Egypt, the Nile River flooded every year providing fertile farmland in the desert.
• The Egyptians developed irrigation and other techniques to control Nile floodwaters.
• Egyptians embalmed their pharaohs and built great pyramids as tombs so that the pharaohs would make it to the after life.
• Egyptians used papyrus and hieroglyphics to record history.
• The pharaoh was considered both king and god.
• Massive pyramids were built as tombs for pharaohs.
• The Egyptians developed irrigation and other techniques to control Nile floodwaters.
• Egyptians embalmed their pharaohs and built great pyramids as tombs so that the pharaohs would make it to the after life.
• Egyptians used papyrus and hieroglyphics to record history.
• The pharaoh was considered both king and god.
• Massive pyramids were built as tombs for pharaohs.
The Ancient Hebrews

the Torah
• Judaism was the first monotheistic religion. [belief in one god]
• According to tradition, Moses received the Ten Commandments from God.
• The Ten Commandments became the basis for civil and religious laws of Judaism.
• The Torah is the holy book of Judaism. The Torah is the first five books of the Bible.
• Judaism focused on the belief in one God, the observance of law, practice of the concepts of righteousness and justice, and importance of study of the Torah and Talmud
• According to tradition, Moses received the Ten Commandments from God.
• The Ten Commandments became the basis for civil and religious laws of Judaism.
• The Torah is the holy book of Judaism. The Torah is the first five books of the Bible.
• Judaism focused on the belief in one God, the observance of law, practice of the concepts of righteousness and justice, and importance of study of the Torah and Talmud
Ancient India

• India’s first major religion was Hinduism, which involved a universal spirit called Brahman. The worship of this spirit is sometimes called Brahmanism.
• The caste system organized Indians into four classes - the Brahmins (teachers, scholars and priests), the Kshatriyas (kings and warriors), the Vaishyas (traders), and Sudras (agriculturists, service providers, and some artisan groups).
• The Buddha’s life and teachings, such as honesty, non-violence, and compassion, created a new religion called Buddhism, which spread throughout India to Central Asia.
• The Buddha's Four Noble Truths:
1. Life is suffering
2. People suffer because of desire
3. The only way not to suffer is to have no desires
4. The Eightfold Path is the way to end suffering and end the cycle of reincarnation
• India developed great literature in Sanskrit, such as the Bhagavad Gita, and developed algebra, and the zero.
• The caste system organized Indians into four classes - the Brahmins (teachers, scholars and priests), the Kshatriyas (kings and warriors), the Vaishyas (traders), and Sudras (agriculturists, service providers, and some artisan groups).
• The Buddha’s life and teachings, such as honesty, non-violence, and compassion, created a new religion called Buddhism, which spread throughout India to Central Asia.
• The Buddha's Four Noble Truths:
1. Life is suffering
2. People suffer because of desire
3. The only way not to suffer is to have no desires
4. The Eightfold Path is the way to end suffering and end the cycle of reincarnation
• India developed great literature in Sanskrit, such as the Bhagavad Gita, and developed algebra, and the zero.
Ancient China

The Great Wall
• Confucius taught the importance of duty and respect for family.
• Confucius lived in a time when the government was struggling to run society and when many people were not following the ancient traditions. Confucius wanted to improve society through teaching people to do their duty and honor their parents.
• Respect for elders, proper conduct, and the proper behavior of rulers are key elements of Confucianism.
• Taoists follow the teachings of Laozi, and believe people should give up worldly desires and follow the force that guides all things—the Tao.
• Taoism stressed that everything in life should be in harmony with nature.
• Emperor Shihuangdi united much of China under one dynasty.
• Shi Huangdi created one currency, built roads and a huge canal, and the Great Wall.
• Under the Han dynasty, the civil service exam created a government run by scholars.
• The Han rulers continued to expand the empire and ruled in a period of much peace.
• The Han dynasty also developed the Silk Road and began a trading network that reached much of Asia and the West, including Rome.
• The Silk Road brought new goods and ideas to China.
• Buddhism reached China during the A.D. 100's by monks traveling along the Silk Road.
• Buddhism began as an important religion in China after the Han dynasty collapsed.
• Confucius lived in a time when the government was struggling to run society and when many people were not following the ancient traditions. Confucius wanted to improve society through teaching people to do their duty and honor their parents.
• Respect for elders, proper conduct, and the proper behavior of rulers are key elements of Confucianism.
• Taoists follow the teachings of Laozi, and believe people should give up worldly desires and follow the force that guides all things—the Tao.
• Taoism stressed that everything in life should be in harmony with nature.
• Emperor Shihuangdi united much of China under one dynasty.
• Shi Huangdi created one currency, built roads and a huge canal, and the Great Wall.
• Under the Han dynasty, the civil service exam created a government run by scholars.
• The Han rulers continued to expand the empire and ruled in a period of much peace.
• The Han dynasty also developed the Silk Road and began a trading network that reached much of Asia and the West, including Rome.
• The Silk Road brought new goods and ideas to China.
• Buddhism reached China during the A.D. 100's by monks traveling along the Silk Road.
• Buddhism began as an important religion in China after the Han dynasty collapsed.
Ancient Greece

Parthenon
• The mountains and seas surrounding Greece led to the rise of city-states.
• Each Greek city-state was run by its citizens, or members of the political community.
• The growth of Greece depended on establishing colonies and trade throughout the Mediterranean region.
• A direct democracy involves all citizens in voting and making laws. Most modern democracies are representative; people are elected to represent a group of citizens.
• Sparta developed a militaristic government.
• Athens created a democracy and focused on trade and culture.
• Athens and Sparta joined forces to defeat the Persians in the Persian Wars, but later fought the destructive Peloponnesian War.
•Alexander conquered the Persian Empire and spread Hellenism throughout southwest Asia.
• The Greeks spread their art, architecture, literature, theater, philosophy, and mathematics.
• Some of the great Greek writers include the dramatists Sophocles, Euripides, and Aeschylus.
• Greek ideas of art and architecture influence styles today.
• Greek philosophers tried to answer life’s big questions.
• Each Greek city-state was run by its citizens, or members of the political community.
• The growth of Greece depended on establishing colonies and trade throughout the Mediterranean region.
• A direct democracy involves all citizens in voting and making laws. Most modern democracies are representative; people are elected to represent a group of citizens.
• Sparta developed a militaristic government.
• Athens created a democracy and focused on trade and culture.
• Athens and Sparta joined forces to defeat the Persians in the Persian Wars, but later fought the destructive Peloponnesian War.
•Alexander conquered the Persian Empire and spread Hellenism throughout southwest Asia.
• The Greeks spread their art, architecture, literature, theater, philosophy, and mathematics.
• Some of the great Greek writers include the dramatists Sophocles, Euripides, and Aeschylus.
• Greek ideas of art and architecture influence styles today.
• Greek philosophers tried to answer life’s big questions.
Ancient Rome

Roman Soldier
• The Roman Republic had two classes of citizens, the patricians (nobles), and the plebeians (common people).
• The Republic had three branches of government: The consuls, who were the chief executives, the senate, who made the laws, and praetors, who were judges.
• Julius Caesar, a Roman general, was named dictator for life. He had many reform ideas, but was assassinated by senators were afraid of his gaining too much power.
• Augustus was Caesar's grand nephew. He became Rome's first emperor. Under his rule, Rome expanded and enjoyed a period of peace.
• Jesus of Nazareth preached love, compassion, and forgiveness. He often taught using stories called parables.
• Early church leaders taught that people could gain salvation through Jesus, who was the messiah.
• Jesus made many enemies in Rome, and was put to death.
• Accounts of his resurrection, or rising from the dead form the basis of Christian belief that Jesus was the son of God.
• St. Paul the Apostle led the early church and its teaching that Jesus was the son of God and the Holy Trinity, the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit.
• The Republic had three branches of government: The consuls, who were the chief executives, the senate, who made the laws, and praetors, who were judges.
• Julius Caesar, a Roman general, was named dictator for life. He had many reform ideas, but was assassinated by senators were afraid of his gaining too much power.
• Augustus was Caesar's grand nephew. He became Rome's first emperor. Under his rule, Rome expanded and enjoyed a period of peace.
• Jesus of Nazareth preached love, compassion, and forgiveness. He often taught using stories called parables.
• Early church leaders taught that people could gain salvation through Jesus, who was the messiah.
• Jesus made many enemies in Rome, and was put to death.
• Accounts of his resurrection, or rising from the dead form the basis of Christian belief that Jesus was the son of God.
• St. Paul the Apostle led the early church and its teaching that Jesus was the son of God and the Holy Trinity, the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit.
